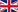
CIRCULAR CLARIFIERS
MODELS circular-clarifiers
EM29 - PERIPHERAL DRIVE – SUCTION TYPE SCRAPER BRIDGE FOR CIRCULAR TANK
| Application | Clarifying of secondary waste water |
| Types | Simple peripheral drive R+1/3 peripheral drive Double peripheral drive |
| Characteristics | The equipment consists of a rotating bridge with scrapers equipped with suction pipes. |
| Operation | The water to be treated flows into the diffusion drum where the kinetic energy is slowed down, the sedimentable solids settle on the tank bottom and are sucked by the suction pipes equipped with regulating telescopic valves. |
| Materials | Hot dip galvanized carbon steel or Stainless steel |
| Installation | In a concrete tank |
| Tank diametre | From 8 to 60 m. |
| Optionals | Scum removal system |
PRINCIPLES OF SIZING
Sludge suction unit sizing.
For the project of the sludge suction unit we have to make sure that the sludge is quickly removed from the tank bottom because if it tends to settle or get too thick for staying in the tank for a too long time, it may happen that: • a part of the recycled sludge returns to the oxidation tank when it is no more fresh and this will affect the treatment efficiency • a shortage of dissolved oxygen may cause a leakage of sludge in the effluent
Mechanical Sizing
Same principles as described for the Peripheral drive scraper bridge mod. EM17.
OPERATION DESCRIPTION
The bottom of the suction scraper bridge tank is flat and the suction pipes, sized according to sludge recycle flow rate, are placed at a distance which does not exceed 3 m. The sludge is conveyed towards the suction pipe by V-shaped scrapers which make the flowing of the sludge towards the piping much easier. Each suction pipe is equipped with a telescopic valve to regulate the flow into the hopper.
The quality and quantity of sludge sucked by each pipe can be checked from the bridge.
The sludge flows into the hopper according to the principle of the communicating vessels.
The sludge flow rate depends on the difference of level between the water surface and the sludge level in the hopper.
The sludge sucked by all of the suction pipes is conveyed out of the tank by means of a self-regulating siphon.
The triggering of the siphon can be made during the commissioning phase by means of a pump or ejector.
TECHNICAL AND DIMENSIONAL DATA NECESSARY TO MAKE A TECHNICAL PROPOSAL AND QUOTATION
| 1. | Flow rate to the sedimentation tank (total) | : m3/h |
| 2. | Flow rate coming from the sedimentation tank (at the overflow weir) | : m3/h |
| 3. | Flow rate of sludge coming from the sedimentation tank | : m3/h |
| 4. | Tank diameter | : m. |
| 5. | Diameter of the feed pipe | : mm. |
| 6. | Sludge level in the drain well | : +m. |
| 7. | Water level in the sedimentation tank | : +m. |